Jupiter’s 2025 Opposition: Observing Its 4 Largest Moons

Jupiter’s 2025 opposition offers an exceptional chance for amateur astronomers to observe its four largest moons, the Galilean satellites, with readily available home telescopes.
The celestial dance of Jupiter and its magnificent retinue has captivated humanity for centuries. In 2025, a particularly favorable alignment, known as opposition, will provide an unparalleled opportunity for skywatchers to delve into the Jovian system. This guide focuses on maximizing your viewing experience, especially when observing Jupiter’s four largest moons with home telescopes, ensuring you don’t miss this spectacular cosmic event.
Understanding Jupiter’s Opposition in 2025
Jupiter’s opposition is a pivotal moment for observers, marking the point when the gas giant is directly opposite the Sun in our sky. This alignment means Jupiter is at its closest approach to Earth for the year, appearing at its brightest and largest in our telescopes. For 2025, this celestial arrangement promises extraordinary viewing conditions, making it an ideal time to explore not just the planet itself, but also its fascinating moon system.
During opposition, Jupiter rises around sunset and sets around sunrise, remaining visible throughout the entire night. This extended viewing window is crucial for amateur astronomers, as it allows ample time to set up equipment, acclimatize to the dark, and conduct prolonged observations. The increased apparent size of Jupiter also means that even modest home telescopes can reveal significant details on the planet’s surface and, more importantly, provide clear views of its four largest moons: Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
Why 2025 is Special for Jupiter Observation
- Peak Brightness: Jupiter will shine at its absolute brightest, cutting through light pollution more effectively.
- Largest Apparent Size: The planet’s closer proximity to Earth means it appears larger through a telescope, enhancing detail.
- All-Night Visibility: Being opposite the Sun, Jupiter is visible from dusk till dawn, offering extensive observation periods.
The significance of opposition extends beyond mere proximity. The direct illumination from the Sun means that Jupiter’s features, and those of its moons, are fully lit from our perspective, minimizing shadows and maximizing contrast. This is especially beneficial for discerning the subtle features on the Galilean moons, which can otherwise be challenging to resolve. Understanding these conditions is the first step in preparing for a truly memorable observing session.
Choosing and Preparing Your Home Telescope
Selecting the right telescope is crucial for a rewarding observation of Jupiter and its moons. While high-end instruments offer unparalleled views, even entry-level home telescopes can provide impressive results during opposition. The key is to understand your equipment’s capabilities and optimize its performance. Refractor telescopes, known for their sharp, high-contrast images, are excellent for planetary viewing, while reflector telescopes offer larger apertures for gathering more light, revealing fainter details.
Before you even point your telescope skyward, ensure it is properly collimated. Collimation, the alignment of the optical elements, is vital for achieving sharp images, especially at higher magnifications required for planetary and lunar observation. Many online guides and videos can walk you through this process, which often requires only a few simple tools and a bit of patience. A well-collimated telescope can make a significant difference in the clarity of your views.
Essential Telescope Accessories for Jupiter Viewing
- Eyepieces: A range of eyepieces (low, medium, and high power) allows you to adjust magnification for different viewing conditions and targets.
- Barlow Lens: This accessory effectively doubles or triples the magnification of your eyepieces, offering more detailed views.
- Filters: Color filters can enhance contrast on Jupiter’s cloud bands and reveal more detail on its moons. A light green or blue filter is often recommended for Jupiter.
Beyond the telescope itself, proper preparation includes finding a dark observing site away from city lights if possible. While Jupiter is bright enough to be seen from urban areas, darker skies will improve the contrast and allow for better views of the moons, especially when they are close to Jupiter’s disk. Allow your telescope to cool down to ambient temperature for at least 30 minutes before observing; this thermal equilibrium prevents image distortion caused by air currents within the telescope tube. With the right equipment and preparation, you’ll be well-positioned to enjoy Jupiter’s 2025 opposition.
Locating Jupiter and Its Galilean Moons
Locating Jupiter during its 2025 opposition will be relatively straightforward, as it will be one of the brightest objects in the night sky. However, effectively finding and tracking its four largest moons requires a bit more precision and familiarity with celestial navigation. Fortunately, numerous tools and techniques can assist amateur astronomers in pinpointing these tiny, yet captivating, worlds.
Start by using a sky chart or a stargazing app on your smartphone or tablet. These tools can accurately show Jupiter’s position in the constellation it currently resides in, as well as the real-time positions of Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. Many apps also offer animated simulations of the moons’ movements, which can be incredibly helpful for anticipating transits, occultations, and eclipses – events where the moons pass in front of, behind, or through Jupiter’s shadow.
Tips for Pinpointing the Moons
- Low Magnification First: Begin with your lowest power eyepiece to locate Jupiter and its immediate surroundings. The moons will appear as tiny, star-like points flanking the planet.
- Gradual Magnification: Once Jupiter and its moons are centered, gradually increase magnification with higher power eyepieces or a Barlow lens.
- Steady Tracking: For manual telescopes, gently nudge the scope to keep Jupiter centered. Motorized mounts will track automatically, allowing for more relaxed observation.
Observing the Galilean moons is a dynamic experience. Their positions change visibly over just a few hours. Io, being the closest to Jupiter, moves the fastest, sometimes completing a full orbit in less than two days. Ganymede and Callisto, further out, have slower, more leisurely orbits. By observing over several nights, you can witness their balletic motion, a testament to Galileo’s groundbreaking observations centuries ago. Patience and repeated viewing sessions will reveal the intricate dance of these distant worlds.
Observing Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto
Each of Jupiter’s four largest moons – Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto – presents a unique set of observational challenges and rewards. While they will appear as mere pinpricks of light through most home telescopes, their relative positions, brightness, and occasional phenomena like transits, occultations, and eclipses make them endlessly fascinating. During the 2025 opposition, with Jupiter at its best, these events will be particularly striking.
Io, the innermost of the Galilean moons, is known for its intense volcanic activity. Through a telescope, it often appears subtly yellowish due to sulfurous compounds. Europa, slightly smaller than Io, is believed to harbor a vast subsurface ocean, making it a prime target in the search for extraterrestrial life. It typically appears as a bright, icy-white speck. Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system, even larger than the planet Mercury, exhibits a grayish hue and can sometimes show faint surface markings with larger amateur telescopes. Callisto, the outermost, is usually the dimmest and appears grayish-brown, often described as having a heavily cratered, ancient surface.
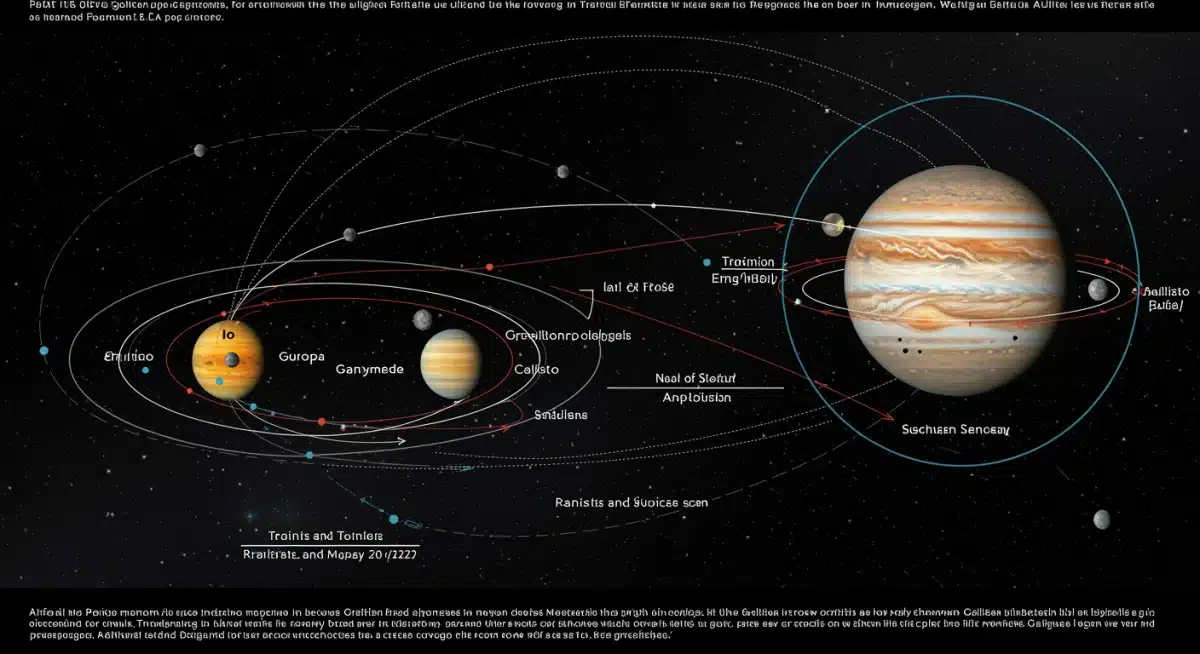
Observing these moons is not just about seeing them, but understanding their dynamic interactions. Keep an eye out for:
Key Phenomena to Look For
- Transits: A moon passing directly in front of Jupiter’s disk, sometimes casting a shadow.
- Occultations: A moon disappearing behind Jupiter.
- Eclipses: A moon passing into Jupiter’s shadow, dimming or disappearing entirely.
- Conjunctions: Two or more moons appearing very close together.
Predicting these events requires consulting an ephemeris or using a specialized astronomy app. Witnessing a moon’s shadow transit across Jupiter’s cloud tops is an especially rewarding sight, offering a sense of the immense scale and motion within our solar system. The 2025 opposition will provide numerous opportunities for such observations, turning your home telescope into a portal to distant cosmic drama.
Enhancing Your Viewing Experience: Tips and Tricks
Beyond basic equipment and location, several advanced techniques and considerations can significantly enhance your observation of Jupiter and its moons during the 2025 opposition. These tips range from optimizing your observing environment to improving your visual acuity, ensuring you capture as much detail as possible from this spectacular celestial event.
One of the most critical factors is atmospheric seeing – the steadiness of Earth’s atmosphere. Turbulent air, often caused by heat radiating from buildings or pavement, can blur telescopic images. Observing on nights with stable, calm air, often after midnight when the ground has cooled, will yield sharper views. Avoid looking over rooftops or asphalt that has been baking in the sun all day. A clear, moonless night is always preferable, though Jupiter’s brightness means some moonlight won’t entirely ruin the view.
Practical Tips for Sharper Views
- Dark Adaptation: Allow your eyes at least 20-30 minutes to adapt to the dark before observing to maximize sensitivity.
- Avoid High Magnification in Poor Seeing: If the atmosphere is turbulent, lower magnification will often provide a clearer, albeit smaller, image.
- Patience and Sketching: Don’t rush. Take your time, let details emerge, and consider sketching what you see. This improves observation skills.
Another often-overlooked aspect is observer comfort. A comfortable observing chair can make a huge difference during long sessions, reducing fatigue and allowing for sustained focus. Keeping a logbook of your observations, noting atmospheric conditions, equipment used, and what you saw, can also be incredibly rewarding. This documentation not only tracks your progress but also helps you learn what works best under various conditions. By integrating these practices, you’ll transform a simple viewing into a profound astronomical experience.
Photography and Documentation of Jupiter and Its Moons
Beyond visual observation, the 2025 Jupiter opposition offers a fantastic opportunity for astrophotography. Capturing images of Jupiter and its Galilean moons with your home telescope can be a challenging yet immensely rewarding endeavor, allowing you to share your cosmic discoveries and document the dynamic changes within the Jovian system. Even with modest equipment, impressive results are achievable with the right techniques.
For beginners, simply holding a smartphone camera up to the eyepiece can yield surprisingly decent results, especially for capturing the moons as distinct points of light. However, for more detailed images of Jupiter’s cloud bands and the moons’ subtle features, a dedicated planetary camera or a DSLR attached to the telescope is recommended. These cameras can capture video at high frame rates, which is then processed using specialized software to stack the best frames, reducing atmospheric distortion and enhancing detail.
Essential Astrophotography Gear and Techniques
- Planetary Camera: High-frame-rate cameras like ZWO ASI or similar models are ideal for capturing video of planets.
- Barlow Lens (for imaging): Often used to increase the effective focal length of the telescope, making Jupiter appear larger on the camera sensor.
- Image Stacking Software: Programs like AutoStakkert!, Registax, and Photoshop are crucial for processing video frames into sharp, detailed images.
- Motorized Mount: Essential for tracking Jupiter accurately during video capture, preventing drift.
When photographing, capture several short videos rather than one long one, as atmospheric conditions can change rapidly. Experiment with exposure settings and gain to avoid overexposing Jupiter’s bright disk while still capturing the fainter moons. Post-processing is where the magic happens, allowing you to bring out details not immediately apparent in raw footage. Documenting your observations, whether through photography or detailed sketches, preserves the memory of this special opposition and contributes to your personal astronomical journey. Sharing your images with online communities can also provide valuable feedback and connect you with fellow enthusiasts.
| Key Aspect | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 2025 Opposition | Jupiter is closest to Earth and brightest, offering optimal viewing conditions for the planet and its moons. |
| Galilean Moons | Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto are visible as distinct points of light, even with modest home telescopes. |
| Telescope Preparation | Ensure proper collimation, allow cool-down, and use appropriate eyepieces and filters for best results. |
| Dynamic Events | Look for transits, occultations, and eclipses of the moons, which change hourly. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Jupiter’s 2025 Opposition
Jupiter’s opposition occurs when the planet is directly opposite the Sun from Earth’s perspective. This makes Jupiter appear its brightest and largest in the night sky, offering optimal viewing conditions for observers with telescopes and even the naked eye.
Even a modest home telescope, such as a 60mm refractor or an 8-inch reflector, can reveal Jupiter’s four largest moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto) as distinct points of light. Larger apertures will provide more detail and brightness.
Yes, with a 6-inch or larger telescope and good atmospheric seeing, you can often discern the Great Red Spot. Using color filters, like a light blue or green, can enhance its visibility and bring out more detail in Jupiter’s cloud bands during opposition.
Jupiter’s opposition occurs approximately every 13 months. This regular cycle is due to the different orbital periods of Earth and Jupiter around the Sun. Each opposition presents a unique viewing opportunity, with varying celestial alignments.
Optimal conditions include clear, stable atmospheric seeing, minimal light pollution, and allowing your telescope to acclimate to outdoor temperatures. Observing when Jupiter is high in the sky also reduces atmospheric distortion, providing sharper views of the planet and its moons.
Conclusion
The Jupiter 2025 opposition is more than just another astronomical event; it’s a prime opportunity for both seasoned and novice skygazers to connect with the cosmos. By preparing your home telescope, understanding the dynamics of Jupiter’s Galilean moons, and applying practical observing tips, you can transform a simple night out into an unforgettable journey through our solar system. This guide has aimed to equip you with the knowledge needed to make the most of this celestial spectacle, encouraging you to step outside, look up, and witness the grandeur of Jupiter and its captivating lunar companions. May your observations be clear and your wonder boundless.





